How Often Should You Reposition A Patient In Bed
Ronan Farrow
Mar 23, 2025 · 3 min read
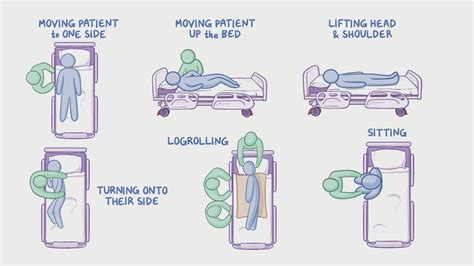
Table of Contents
How Often Should You Reposition a Patient in Bed? A Guide for Caregivers
Repositioning a patient in bed is a crucial aspect of patient care, significantly impacting their comfort, preventing complications, and promoting overall well-being. The frequency of repositioning depends on several factors, and there's no single "one-size-fits-all" answer. This guide will delve into the importance of repositioning, the factors influencing frequency, and best practices to ensure patient safety and comfort.
Why is Repositioning Important?
Regular repositioning offers numerous benefits, including:
-
Preventing Pressure Ulcers (Pressure Sores): Prolonged pressure on the skin restricts blood flow, leading to skin breakdown and the formation of pressure ulcers. Repositioning helps redistribute pressure, preventing these painful and potentially serious wounds. This is arguably the most critical reason for regular repositioning.
-
Improving Circulation: Maintaining good circulation is vital for overall health. Repositioning helps prevent blood pooling, reducing the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and other circulatory problems.
-
Enhancing Respiratory Function: Changing positions helps clear the lungs of secretions, preventing respiratory complications like pneumonia and atelectasis (collapsed lung).
-
Increasing Comfort and Reducing Pain: Staying in one position for too long can lead to discomfort, stiffness, and pain. Regular repositioning allows for better muscle relaxation and reduces pressure points.
-
Preventing Contractures: Prolonged immobility can lead to joint contractures (shortening and tightening of muscles and tendons), limiting mobility and range of motion. Repositioning helps prevent this.
Factors Influencing Repositioning Frequency
The ideal frequency of repositioning varies greatly depending on several factors:
-
Patient's Condition: Patients with limited mobility, impaired sensation, or existing pressure ulcers require more frequent repositioning than those who are mobile and alert.
-
Medical History: Pre-existing conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and peripheral vascular disease can increase the risk of pressure ulcers and necessitate more frequent repositioning.
-
Type of Support Surface: Using pressure-relieving mattresses and cushions can extend the time between repositioning. However, regular repositioning remains essential even with specialized support surfaces.
-
Level of Activity: Patients who are able to move independently may require less frequent repositioning than those who are completely immobile.
-
Individual Needs: Every patient is unique. Some individuals may experience discomfort or pain with certain positions, necessitating more frequent adjustments.
Recommended Repositioning Schedules & Techniques
While there's no universally accepted schedule, here are some general guidelines:
-
Every 2 Hours: This is often recommended for patients at high risk of pressure ulcers or those with limited mobility.
-
Every 4 Hours: For patients with moderate risk, repositioning every four hours might suffice. However, frequent assessment is crucial.
-
As Needed: Even for patients with lower risk, repositioning should occur "as needed" if discomfort or pressure points are detected.
Techniques:
-
Proper Body Mechanics: Always use proper body mechanics to avoid injury to yourself and the patient.
-
Gentle Movements: Reposition the patient slowly and gently to minimize discomfort and prevent injury.
-
Support Surfaces: Use pillows, rolled blankets, and other support surfaces to maintain proper body alignment.
-
Assess the Skin: Before and after repositioning, carefully assess the patient's skin for any signs of redness, breakdown, or pressure ulcers.
Conclusion: Communication and Observation are Key
The frequency of repositioning is a critical element of patient care. Close observation, regular assessment, and careful consideration of the individual patient's needs are paramount. Communicate with the healthcare team to develop an appropriate repositioning schedule tailored to each patient’s specific circumstances. Regular monitoring and proactive repositioning can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve the patient’s overall quality of life. Remember, prevention is better than cure.
Featured Posts
Also read the following articles
| Article Title | Date |
|---|---|
| How Much Is Busch Peach | Mar 23, 2025 |
| How To Cancel Palmera Vacation Club | Mar 23, 2025 |
| How To Buy Plants From Wholesale Nursery | Mar 23, 2025 |
| How Much Meat Off A Deer | Mar 23, 2025 |
| How To Become A Templar | Mar 23, 2025 |
Latest Posts
-
How Many Airports Are In Kansas
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Many Advanced Sommeliers Are There
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Many Acres Is Glamis Sand Dunes
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Many Acres Can You Buy With 1 Million Dollars
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Many 8 Inch Blocks In A Queen Size Quilt
Apr 06, 2025
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Often Should You Reposition A Patient In Bed . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
