How To Find Acceleration And Velocity
Ronan Farrow
Feb 24, 2025 · 3 min read
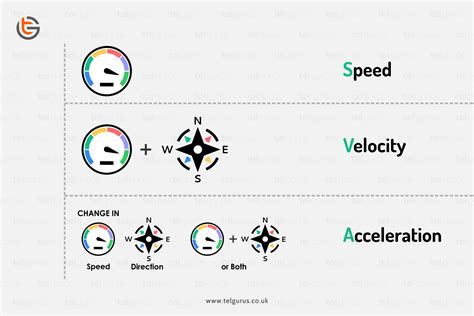
Table of Contents
How to Find Acceleration and Velocity: A Complete Guide
Understanding velocity and acceleration is fundamental to grasping the concepts of motion in physics. While seemingly complex, mastering these concepts is achievable with a structured approach. This guide breaks down how to find both velocity and acceleration, providing clear examples and helpful tips.
What is Velocity?
Velocity describes the rate of change of an object's position. It's a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude (speed) and direction. A car traveling at 60 mph north has a different velocity than a car traveling at 60 mph south, even though their speeds are the same.
Formula for Velocity:
Velocity (v) = Displacement (Δx) / Time (Δt)
- Displacement (Δx): The change in position of an object. It's the final position minus the initial position. It's crucial to remember that displacement is a vector quantity, so direction matters.
- Time (Δt): The time taken for the displacement to occur.
Example: A car travels 100 meters east in 10 seconds. Its velocity is:
v = 100 m / 10 s = 10 m/s east
What is Acceleration?
Acceleration describes the rate of change of an object's velocity. Like velocity, it's a vector quantity. This means a change in speed or direction constitutes acceleration.
Formula for Acceleration:
Acceleration (a) = Change in Velocity (Δv) / Time (Δt)
- Change in Velocity (Δv): The final velocity minus the initial velocity.
- Time (Δt): The time taken for the change in velocity to occur.
Example: A car initially traveling at 10 m/s east accelerates to 20 m/s east in 5 seconds. Its acceleration is:
a = (20 m/s - 10 m/s) / 5 s = 2 m/s² east
Notice the units for acceleration are m/s². This represents "meters per second per second," indicating how much the velocity changes each second.
Finding Velocity and Acceleration in Different Scenarios
The calculations above are for uniform motion (constant velocity and constant acceleration). However, real-world scenarios are often more complex. Let's look at a few:
1. Non-Uniform Motion (Changing Acceleration):
In situations with changing acceleration, calculus (specifically, integration and differentiation) becomes necessary. However, for simpler cases where acceleration changes linearly, you can often find an average acceleration over a given time interval.
2. Projectile Motion:
Projectile motion involves objects moving under the influence of gravity. The vertical acceleration is always due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s² downwards), while the horizontal acceleration is typically zero (ignoring air resistance). Using appropriate kinematic equations, you can find the velocity and acceleration components in both the x and y directions.
3. Using Graphs:
Velocity-time graphs provide a powerful visual tool for analyzing motion. The slope of the velocity-time graph represents acceleration. The area under the velocity-time graph represents displacement.
Key Considerations and Tips
- Units: Always use consistent units (e.g., meters for distance, seconds for time).
- Direction: Remember that velocity and acceleration are vector quantities; direction matters. Use positive and negative signs to indicate direction (e.g., positive for right/up, negative for left/down).
- Kinematic Equations: For more complex scenarios, utilize the kinematic equations of motion to relate displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time.
- Break Down Complex Problems: If a problem seems overwhelming, break it down into smaller, more manageable parts. Analyze the motion in each part separately, then combine the results.
Mastering velocity and acceleration requires practice and a clear understanding of the underlying concepts. By working through examples and applying the formulas and techniques outlined in this guide, you can confidently tackle a wide range of motion problems. Remember to always pay attention to units and direction for accurate results.
Featured Posts
Also read the following articles
| Article Title | Date |
|---|---|
| How To Hide App Lock On Android | Feb 24, 2025 |
| How To Factor V | Feb 24, 2025 |
| How To Make Google Form Single Choice | Feb 24, 2025 |
| How To Align Text In Excel For Printing | Feb 24, 2025 |
| How To Log Out Google Account From Chrome | Feb 24, 2025 |
Latest Posts
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find Acceleration And Velocity . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
