How To Full Join 3 Tables In Sql
Ronan Farrow
Feb 24, 2025 · 3 min read
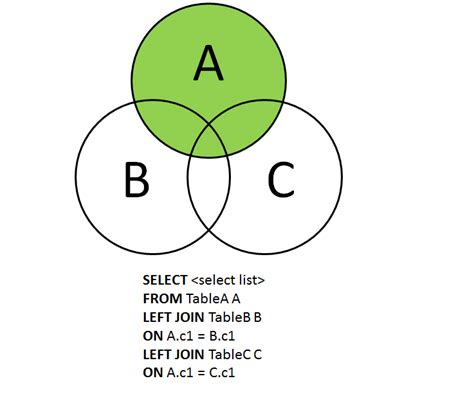
Table of Contents
How to FULL JOIN Three Tables in SQL
Joining multiple tables is a fundamental skill in SQL, crucial for retrieving data from different related tables. While simple JOINs are straightforward, understanding how to perform a FULL OUTER JOIN (often shortened to FULL JOIN) across three or more tables requires a more strategic approach. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process, equipping you with the knowledge and techniques to efficiently query your database.
Understanding FULL JOIN
Before diving into the specifics of joining three tables, let's recap the power of the FULL JOIN. Unlike INNER JOIN which only returns rows where a match exists in all joined tables, a FULL JOIN returns all rows from all participating tables. Where matches exist, the corresponding columns are joined; where there is no match in one or more tables, the missing columns are filled with NULL. This is invaluable when you need a complete picture of your data, including records that may not have relationships in all tables.
Joining Three Tables: The Strategy
Joining three tables effectively involves a stepwise process. It's generally not advisable to attempt a single, complex FULL JOIN statement encompassing all three tables directly. Instead, you'll typically perform a series of joins, usually starting with two tables, and then joining the result with the third.
Here's a structured approach:
-
Choose the Primary Join: Identify the two tables with the most crucial relationship. This will form the foundation of your query.
-
Perform the First FULL JOIN: Execute a
FULL JOINbetween the two tables you selected in step 1. This will combine all rows from both tables, filling inNULLvalues as necessary. -
Join with the Third Table: Take the result from step 2 and perform another
FULL JOINwith the third table. This time, you'll be joining the result set from the previous step with the third table based on appropriate matching columns. -
Refine the Result Set: After the joins are complete, use
WHEREclauses and other filtering techniques to refine the result set and extract precisely the data you need.
Example Scenario and SQL Query
Let's consider an example. Suppose we have three tables:
Customers:CustomerID,CustomerName,CityOrders:OrderID,CustomerID,OrderDate,TotalAmountPayments:PaymentID,OrderID,PaymentDate,AmountPaid
Our goal is to obtain a complete list of customers, their orders, and their payments, even if some customers have no orders, or if some orders have no corresponding payments.
Here's how we can achieve this using a series of FULL JOINs:
SELECT
c.CustomerID,
c.CustomerName,
c.City,
o.OrderID,
o.OrderDate,
o.TotalAmount,
p.PaymentID,
p.PaymentDate,
p.AmountPaid
FROM
Customers c
FULL JOIN
Orders o ON c.CustomerID = o.CustomerID
FULL JOIN
Payments p ON o.OrderID = p.OrderID;
This query first joins Customers and Orders, then joins the result with Payments. This approach provides a complete dataset, handling all scenarios—customers without orders, orders without payments, and so on.
Optimizing FULL JOINs
Remember, FULL JOIN operations can be resource-intensive, particularly with large datasets. Consider these optimization strategies:
- Indexing: Ensure appropriate indexes are created on the columns involved in the joins to speed up the query process.
- Filtering: Employ
WHEREclauses to filter data as early as possible in the query to minimize processing. - Data Partitioning: For extremely large databases, consider data partitioning to improve query performance.
By understanding the fundamentals of FULL JOIN and following the strategies outlined above, you'll be able to effectively query data across multiple tables in SQL, unlocking valuable insights from your database. Remember to adapt this approach to your specific table structures and relationships. Practice makes perfect; experiment with different join combinations to master this essential SQL technique.
Featured Posts
Also read the following articles
| Article Title | Date |
|---|---|
| How To Draw Muscles | Feb 24, 2025 |
| How To Know Your Face Shape Male App | Feb 24, 2025 |
| How To See Who Has Unfollowed You On Instagram 2024 | Feb 24, 2025 |
| How To Enable Airdrop On Mac | Feb 24, 2025 |
| How To Make Fried Rice Like Panda Express | Feb 24, 2025 |
Latest Posts
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Full Join 3 Tables In Sql . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
