How To Read Air Fuel Gauge
Ronan Farrow
Mar 25, 2025 · 3 min read
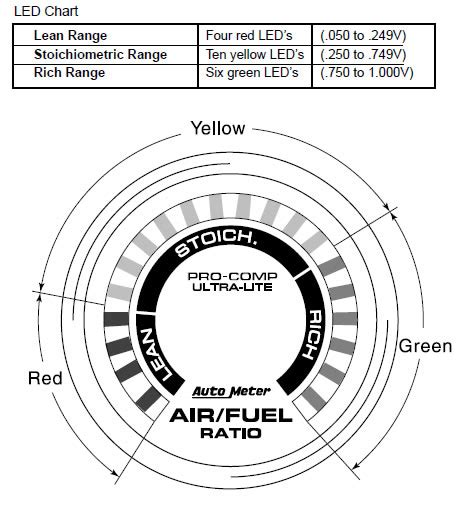
Table of Contents
How to Read an Air Fuel Gauge: A Comprehensive Guide
Knowing how to interpret your air fuel ratio (AFR) gauge is crucial for optimizing your engine's performance and fuel efficiency. This guide will walk you through understanding the different readings and what they signify for your vehicle. We'll cover everything from understanding the basics of AFR to troubleshooting potential problems.
Understanding the Air Fuel Ratio (AFR)
The air-fuel ratio is the proportion of air to fuel in the combustion process of your engine's cylinders. It's expressed as a ratio, for example, 14.7:1. This means 14.7 parts of air to 1 part of fuel. This is considered the stoichiometric ratio – the ideal ratio for complete combustion.
What Does the Gauge Show?
An AFR gauge typically displays the ratio as a numerical value. Some gauges may also use a color-coded display to indicate richer or leaner mixtures. Understanding these visual cues is vital.
Interpreting Your Air Fuel Gauge Readings
The ideal AFR is around 14.7:1, but depending on your engine's configuration and operating conditions, slight variations are normal. However, significant deviations from this value indicate potential problems.
AFR Readings and Their Meanings:
- 14.7:1 (Stoichiometric): This is the ideal ratio for complete combustion, maximizing fuel efficiency and minimizing emissions.
- Below 14.7:1 (Rich Mixture): This means there's more fuel than air in the combustion chamber. Symptoms may include black smoke from the exhaust, decreased fuel economy, and potential engine damage over time. This can be caused by faulty oxygen sensors, fuel injectors delivering too much fuel, or a malfunctioning mass airflow sensor.
- Above 14.7:1 (Lean Mixture): This indicates there's more air than fuel. Symptoms may include pinging or knocking, reduced power, and increased engine temperature. Potential causes include a leak in the intake system, faulty fuel pump, clogged fuel filter, or a malfunctioning mass airflow sensor.
Troubleshooting Based on AFR Readings
If your AFR gauge shows a consistently rich or lean mixture, it's crucial to investigate the potential causes. While a mechanic's expertise is always recommended for complex issues, some common problems can be checked:
Common Causes of Rich Mixtures:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: This sensor monitors the exhaust gases and sends signals to the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the fuel-air mixture. A malfunctioning sensor can lead to a rich mixture.
- Clogged Fuel Injectors: Clogged injectors may deliver more fuel than intended.
- Faulty Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF): This sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine. A malfunctioning MAF can cause incorrect fuel delivery.
Common Causes of Lean Mixtures:
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the intake system can allow excess air to enter the engine.
- Clogged Fuel Filter: A restricted filter may reduce fuel flow to the engine.
- Faulty Fuel Pump: A weak fuel pump might not supply enough fuel to the engine.
- Faulty Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF): As mentioned before, a malfunctioning MAF can also cause a lean mixture.
Maintaining Your Vehicle for Optimal AFR
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring your engine operates at its optimal air-fuel ratio. This includes:
- Regular Oil Changes: Keeping your engine oil clean helps ensure optimal performance.
- Fuel Filter Replacement: Replacing your fuel filter as recommended in your owner's manual prevents fuel flow restrictions.
- Professional Inspections: Regular check-ups by a qualified mechanic can identify and address potential issues before they become major problems.
By understanding how to read your air-fuel gauge and addressing any deviations from the ideal ratio, you can keep your engine running smoothly, efficiently, and for a longer time. Remember, consulting a professional mechanic is always recommended for diagnosing and repairing complex engine problems.
Featured Posts
Also read the following articles
| Article Title | Date |
|---|---|
| How To Prepare For Kitchen Remodel | Mar 25, 2025 |
| How To Keep Up Humidity In A Terrarium | Mar 25, 2025 |
| How To Install Boat Seats | Mar 25, 2025 |
| How To Make Loaded Tea | Mar 25, 2025 |
| How To Remove A Stripped Caliper Bolt | Mar 25, 2025 |
Latest Posts
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Read Air Fuel Gauge . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
